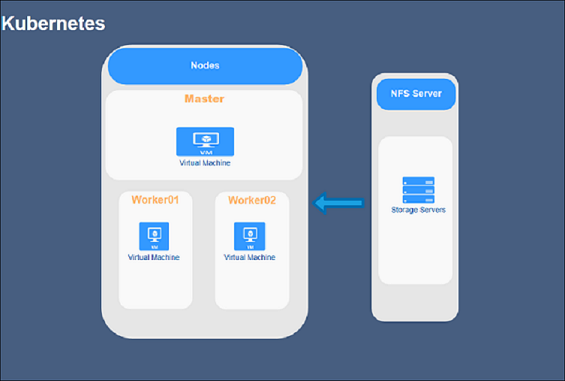
The objective of this post is to implement a basic hyperledger Block Chain network on Kubernetes platform. The indent is to understand the architecture behind kubernetes deployment along with docker and the concept of docker inside and docker container.
For K8s we will be deploy one master node , two worker nodes and a NFS server to share network artifacts and chain code data across the nodes.
Keeping it simple we will be deploying the Hyperledger Fabric network consisting of one organization, maintaining one peer node, one orderer with ‘solo’ ordering service. We will create a channel , join peer to the channel , install chaincode on peer and instantiate chaincode on channel. Also invoke transactions against the deployed chaincode.
Installation
Install Kubernetes ,initialize cluster, add worker nodes to the Kubernetes Cluster.We will mount PersistantVolumes as NFS.Configureyour NFS file server VM and mount the NFS share on all the nodes.
Generate the Network Artifacts
Generate the network artifacts using configtx.yaml, crypto-config.yaml.If you intent to modify the network topology, change the configuration files (.yaml files) appropriately.
Copy (or use bind) the files from network artifacts , crypto and chaincode directory to NFS share.
Deployment Model
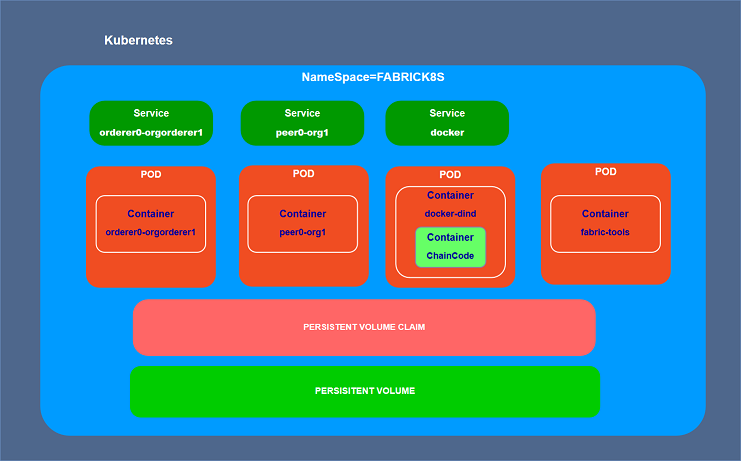
NameSpace
- fabrick8s
Services
- Orderer
- Peer
- Docker Dind
Deployments
- Orderer
- Peer
- Docker Dind ( For ChainCode container Docker in Docker)
- CLI For executing peer commands (Optional — create k8s jobs instead)
Persistent Volume Claim
Persistent Volume ( NFS)
Start the network
Now lets start the network by running scripts one by one.
kubectl create -f 1namespace.yaml
kubectl create -f 2pv-pvc.yaml
kubectl create -f 3orderer0-orgorderer1-deploy.yaml
kubectl create -f 4peer0-org1-deploy.yaml
kubectl create -f 5docker.yaml
kubectl create -f 6docker-volume.yaml
kubectl create -f 7org1-cli-deploy.yaml\Verify the deployments in the dashboard
Create , join , Update Channel
Manually enter into the CLI.
kubectl get pods — all-namespaces
kubectl exec -it cli-2XXXXX3 bash — namespace=fabrick8s\peer channel create -o orderer0-orgorderer1:32000 -c $CHANNEL_NAME -f ./channel-artifacts/channel.tx — outputBlock ./channel-artifacts/rtrchannel01.block
peer channel fetch newest -o orderer0-orgorderer1:32000 -c $CHANNEL_NAME
peer channel join -b ${CHANNEL_NAME}_newest.block
Install ChainCode
peer chaincode install -n rtrcc -v 1.0 -p github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/chaincode/chaincode_example02/go

Instantiate ChainCode
peer chaincode instantiate -o orderer0-orgorderer1:32000 -C $CHANNEL_NAME -n rtrcc -v 1.0 -c ‘{“Args”:[“init”,”a”,”100",”b”,”200"]}’ -P “AND(‘Org1MSP.member’)”

Invoke ChainCode
peer chaincode invoke -C $CHANNEL_NAME -n rtrcc -c ‘{“Args”:[“invoke”,”a”,”b”,”10"]}’
peer chaincode query -C $CHANNEL_NAME -n rtrcc -c ‘{“Args”:[“query”,”a”]}’

You would see that the chain code container is getting started inside the docker-dind pod as a sidecar container.
References
https://applatix.com/case-docker-docker-kubernetes-part-2